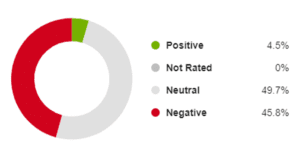
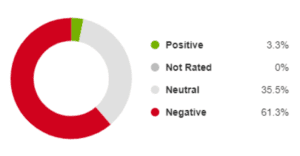
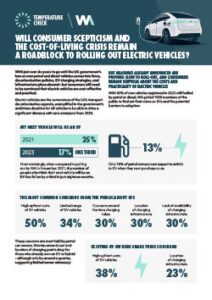
In the last 14 years we’ve had four General Elections, six Prime Ministers and nine Transport Secretaries. We’ve also had consensus among the leaders of the big political parties that HS2 is a good thing and needs to happen. Yes, it has been trimmed along the way, and phases have been delayed, but the idea has survived – and Ministers have been proud to talk about the benefits.
Yesterday all that changed when Rishi Sunak announced he was cancelling the rest of HS2 – everything except Phase 1 from Euston to just north of Birmingham. What’s more he didn’t just cancel it – the way he spoke about it was deliberately critical. HS2 is not just the ‘wrong project’ but the ‘ultimate example of the old consensus’. It’s difficult to imagine any Minister in this Government talking positively about HS2 again.
Here are a few reflections on what this announcement means.
First, the risk premium for new infrastructure in the UK. This is a public sector project but one that has been highly visible around the world. The inward investment strategies of some of our largest cities outside London have been based on it. A whole structure of advice and planning – the National Infrastructure Commission – started at the same time as HS2. Whatever the merits of the decision, investors will see it as another reason to be wary of government. They may think (unfairly) the UK just can’t do infrastructure well. Both major parties could usefully think about how to reassure them.
Second, it’s not just a consensus about HS2 that has gone: transport policy is now more unstable than at any time in the last 15 years. Expect to hear more from the Conservatives about car drivers and private individuals, less about active travel and modal shift; more about towns and suburbs, less about our biggest cities. There’s an obvious political dimension to this but the Prime Minister no doubt believes in it too. It’s also possible to discern another force at work: the Treasury, one institution that consistently opposed HS2. George Osborne overruled his officials when he was Chancellor, but it’s not difficult to imagine their advice to Rishi Sunak – the enormous risks of mega-projects, their poor returns compared to smaller schemes, especially roads.
Third, the Government has now created a huge range of hard questions by its commitment to Network North. Transport infrastructure is complex: it takes years to plan, get consents, design and build successfully. The plan includes everything from extending existing schemes (£2 bus fare) to new projects that sound just as challenging as HS2 (£12 billion for Liverpool-Manchester, over £2 billion for Bradford-Manchester). But the money that has been saved on HS2 would, mostly, not have been spent for years: when will these new projects happen, who will lead them, how will they be funded? Expect DfT to be busy for years answering these questions – and note caveats in the official document about costs, business cases, benefits and funding profile.
Finally, whatever happens to these plans, the transport sector needs to think long and hard about the story it wants to tell, and how to respond to this challenge. Even if Sunak’s term as PM is short, the story he is telling about transport is not going to go away – nor is that old consensus going to re-emerge.